Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plot Chambolle Pock path vs Lasso Tikhonov path¶
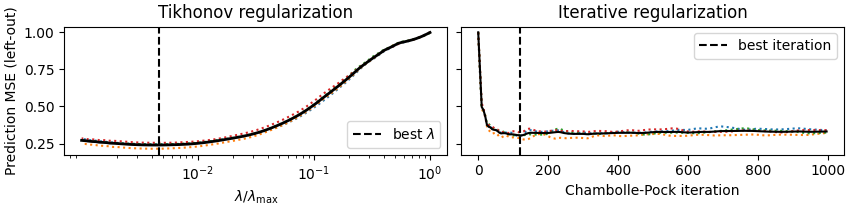
Comparison of Tikhonov regularization path (fast LassoCV with the celer package) and iterative regularization (ours).
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import sparse
from celer import LassoCV
from numpy.linalg import norm
from libsvmdata import fetch_libsvm
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from joblib import Parallel, delayed
from iterreg.sparse import dual_primal
from iterreg.sparse.estimators import SparseIterReg
dataset = 'rcv1.binary'
X, y = fetch_libsvm(dataset)
# make dataset smaller for faster example:
X = X[:5000]
y = y[:5000]
n_splits = 4
kf = KFold(n_splits=n_splits, shuffle=True, random_state=0)
clf = LassoCV(fit_intercept=False, n_jobs=4, cv=kf, verbose=0)
clf.fit(X, y)
max_iter = 1_000
f_store = 5
L = sparse.linalg.svds(X, k=1)[1][0]
sigma_good = 1. / norm(X.T @ y, ord=np.inf)
step_ratio = 0.99 / (L ** 2 * sigma_good ** 2)
n_points = max_iter // f_store
mse_dp = np.zeros((n_points, n_splits))
res = Parallel(n_jobs=-1)(delayed(dual_primal)(
X[train_idx], y[train_idx], step_ratio=step_ratio, max_iter=max_iter,
f_store=f_store, verbose=True)
for train_idx, _ in kf.split(X))
all_w = np.array([result[-1] for result in res])
for split, (train_idx, test_idx) in enumerate(kf.split(X)):
mse_dp[:, split] = np.mean(
(X[test_idx] @ all_w[split].T - y[test_idx, None]) ** 2, axis=0)
best_alpha = clf.alpha_
plt.close('all')
fig, axarr = plt.subplots(
1, 2, sharey=True, figsize=(8.5, 2.1), constrained_layout=True)
ax = axarr[0]
ax.semilogx(clf.alphas_ / clf.alphas_[0], clf.mse_path_, ':')
ax.semilogx(clf.alphas_ / clf.alphas_[0], clf.mse_path_.mean(axis=-1), 'k',
linewidth=2)
ax.axvline(clf.alpha_ / clf.alphas_[0], linestyle='--', color='k',
label=r'best $\lambda$')
ax.set_title("Tikhonov regularization")
ax.set_xticks([1e-2, 1e-1, 1e0])
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\lambda / \lambda_{\mathrm{\max}}$')
ax.set_ylabel('Prediction MSE (left-out)')
ax.legend()
ax = axarr[-1]
ax.set_title("Iterative regularization")
ax.plot(f_store * np.arange(n_points), mse_dp, ':')
ax.plot(f_store * np.arange(n_points), mse_dp.mean(axis=-1), 'k')
best_iter = f_store * np.argmin(np.mean(mse_dp, axis=-1))
ax.axvline(best_iter, linestyle='--', color='k', label='best iteration')
ax.set_xlabel("Chambolle-Pock iteration")
ax.legend()
plt.show(block=False)
Out:
Dataset: rcv1.binary
Downloading data from https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvmtools/datasets/binary/rcv1_train.binary.bz2 (13.1 MB)
file_sizes: 0%| | 0.00/13.7M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
file_sizes: 0%| | 24.6k/13.7M [00:00<01:48, 126kB/s]
file_sizes: 0%| | 49.2k/13.7M [00:00<01:49, 125kB/s]
file_sizes: 1%|2 | 106k/13.7M [00:00<01:07, 201kB/s]
file_sizes: 2%|4 | 221k/13.7M [00:00<00:38, 352kB/s]
file_sizes: 3%|9 | 451k/13.7M [00:00<00:20, 645kB/s]
file_sizes: 7%|#7 | 909k/13.7M [00:01<00:10, 1.22MB/s]
file_sizes: 13%|###4 | 1.83M/13.7M [00:01<00:05, 2.34MB/s]
file_sizes: 27%|######9 | 3.66M/13.7M [00:01<00:02, 4.53MB/s]
file_sizes: 38%|#########9 | 5.23M/13.7M [00:01<00:01, 5.60MB/s]
file_sizes: 50%|############8 | 6.81M/13.7M [00:01<00:01, 6.33MB/s]
file_sizes: 61%|###############8 | 8.38M/13.7M [00:02<00:00, 6.83MB/s]
file_sizes: 72%|##################8 | 9.95M/13.7M [00:02<00:00, 7.18MB/s]
file_sizes: 84%|#####################8 | 11.5M/13.7M [00:02<00:00, 7.42MB/s]
file_sizes: 95%|########################8 | 13.1M/13.7M [00:02<00:00, 7.58MB/s]
file_sizes: 100%|##########################| 13.7M/13.7M [00:02<00:00, 4.96MB/s]
Successfully downloaded file to /home/circleci/celer_data/libsvm/binary/rcv1_train.binary.bz2
Decompressing...
Loading svmlight file...
Now do the timings a posteriori, as if we knew the optimal iteration/lambda
bp = SparseIterReg(max_iter=best_iter, memory=best_iter + 1,
step_ratio=step_ratio)
t0 = time.perf_counter()
bp.fit(X, y)
time_cp = time.perf_counter() - t0
print("Duration for CP: %.3fs" % time_cp)
# default grid:
alpha_max = np.max(np.abs(X.T @ y)) / len(y)
alphas = np.geomspace(1, 1e-3, 100) * alpha_max
alphas_stop = alphas[alphas >= best_alpha]
# time if we stopped at best_alpha:
t0 = time.perf_counter()
clf2 = LassoCV(fit_intercept=False, alphas=alphas_stop,
verbose=0, cv=4, n_jobs=4).fit(X, y)
time_cv = time.perf_counter() - t0
print("CP early stop needs %d iter" % best_iter)
print("LassoCV optimal lambda: %.2e lambda_max" %
(best_alpha / clf2.alphas_[0]))
print("CP time: %.3f s" % time_cp)
print("CV time: %.3f s" % time_cv)
print("CP support size: %d" % (bp.coef_ != 0).sum())
print("CV support size: %d" % (clf.coef_ != 0).sum())
Out:
Duration for CP: 0.676s
CP early stop needs 120 iter
LassoCV optimal lambda: 4.64e-03 lambda_max
CP time: 0.676 s
CV time: 11.574 s
CP support size: 714
CV support size: 1430
Total running time of the script: ( 1 minutes 17.673 seconds)